Can Laturedrianeuro Spread
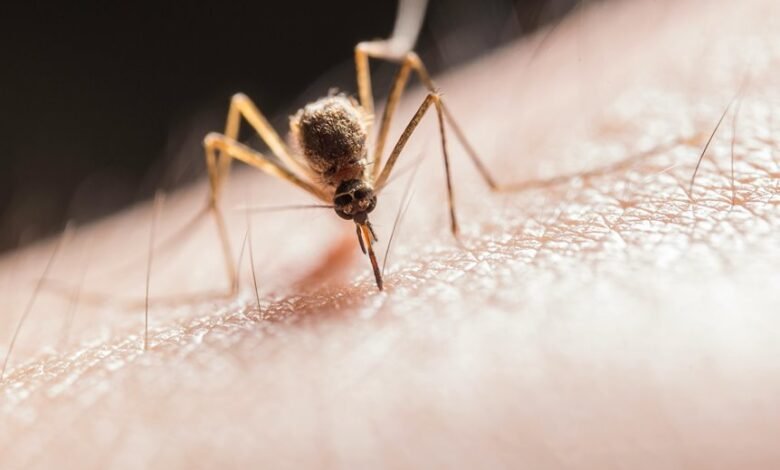
Laturedrianeuro exhibits multiple transmission mechanisms, including direct contact and vector-mediated transfer. These pathways contribute to its spread within diverse populations. Environmental factors and host interactions play significant roles in determining the susceptibility of ecosystems to outbreaks. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing preventive measures. However, the implications of Laturedrianeuro’s spread extend beyond mere transmission, raising questions about the broader ecological impacts and necessary interventions.
Understanding Laturedrianeuro: Characteristics and Behavior
Laturedrianeuro represents a unique genus characterized by distinct morphological and behavioral traits.
This genus exhibits notable host specificity, adapting its physiological mechanisms to interact with particular species.
A symptoms overview reveals a spectrum of responses in affected hosts, including behavioral alterations and physiological disruptions.
Such characteristics underscore the importance of understanding Laturedrianeuro for ecological balance and the implications of its interactions within diverse ecosystems.
Transmission Mechanisms: How Laturedrianeuro Spreads
Understanding the transmission mechanisms of Laturedrianeuro is crucial for comprehending its ecological impact.
The viral life cycle involves multiple transmission routes, including direct contact and vector-mediated transfer. These pathways facilitate the virus’s proliferation within host populations, allowing for widespread dissemination.
Analyzing these mechanisms enhances the understanding of potential outbreaks and informs strategies to mitigate Laturedrianeuro’s spread in diverse ecosystems.
Factors Influencing Spread: Environment and Host Interaction
Although various factors contribute to the spread of Laturedrianeuro, environmental conditions and host interactions play pivotal roles in its transmission dynamics.
Host susceptibility is influenced by genetic and immunological factors, which, when combined with environmental factors such as climate and habitat alterations, can significantly enhance or inhibit the spread of this pathogen.
Ultimately, these factors shape epidemiological patterns across affected regions.
Prevention Strategies: Safeguarding Health Against Laturedrianeuro
Effective prevention strategies are crucial in mitigating the risks associated with Laturedrianeuro transmission.
Central to these efforts are advances in vaccine development, which aim to provide immunity and curb outbreaks.
Additionally, fostering public awareness is essential for educating communities about transmission pathways and protective measures.
Together, these strategies promote informed decision-making, ultimately safeguarding public health and enhancing resilience against future threats.
Conclusion
In summary, the intricate web of Laturedrianeuro’s transmission underscores the delicate balance of ecosystems. Its spread, akin to a silent tide, is shaped by environmental nuances and host dynamics. Vigilant monitoring and proactive strategies are essential to stem this tide, ensuring that the harmony of nature remains intact. As researchers delve deeper into its mechanisms, the hope for effective prevention strategies glimmers on the horizon, promising a safeguard against this enigmatic entity and a healthier future for all.